Basic Information about Cervical Cancer:
Cervical Cancer is a sickness wherein cells in the body outgrow control. Cervical Cancer is constantly named for the piece of the body where it begins, regardless of whether it spreads to other body parts later. At the point when malignant growth begins in the cervix, it is called Cervical Cancer. The cervix associates the vagina (birth waterway) to the upper piece of the uterus. The uterus (or belly) is where a child develops when a lady is pregnant.
Anybody with a cervix is in danger for Cervical malignant growth. It happens most frequently in individuals over age 30. Enduring contamination with particular sorts of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the primary driver of cervical disease. HPV is a typical infection that is passed starting with one individual then onto the next during sex. A big part of physically dynamic individuals will have HPV eventually in their lives, yet couple of ladies will get Cervical Cancer.
Screening tests and the HPV antibody can assist with forestalling Cervical Cancer. At the point when Cervical malignant growth is seen as right on time, it is profoundly treatable and related with long endurance and great personal satisfaction.
Cervical Cancer is the fourth most normal disease in ladies around the world, and it has the fourth most elevated death rate among tumors in women.[1] Most instances of Cervical Cancer are preventable by routine screening and by therapy of precancerous sores. Thus, a large portion of the Cervical Cancer cases are analyzed in ladies who live in locales with deficient screening conventions
Incidence and Mortality;
Estimated new cases and passings from cervical (uterine cervix) disease in the US in 2023:[2]
New cases: 13,960.
Passings: 4,310.
Anatomy;
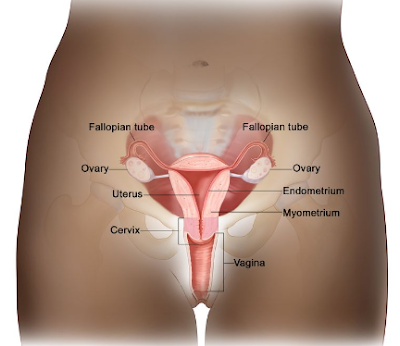
The uterine cervix is adjoining with the uterine body, and it goes about as the opening to the body of the uterus. The uterine cervix is a tube shaped, stringy organ that is a normal of 3 to 4 cm long. The portio of the cervix is the piece of the cervix that is apparent on vaginal examination. The launch of the cervix is named the outside os. The os is the start of the endocervical channel, which frames the internal part of the cervix. At the upper part of the endocervical trench is the inward os, a limiting of the endocervical channel. The restricting imprints the progress from the cervix to the uterine body. The endocervical trench past the inward os is named the endometrial waterway.
The cervix is lined by two sorts of epithelial cells: squamous cells at the external angle, and columnar, glandular cells along the internal trench. The change between squamous cells and columnar cells is a region named the squamocolumnar intersection. Most precancerous and carcinogenic changes emerge in this zone.
Pathogenesis;
Cervical carcinoma has its starting points at the squamocolumnar intersection; it can include the external squamous cells, the internal glandular cells, or both. The forerunner sore is dysplasia: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or adenocarcinoma in situ, which can in this way become obtrusive disease. This interaction can be very sluggish. Longitudinal examinations have shown that in patients with untreated in situ cervical malignant growth, 30% to 70% will foster obtrusive carcinoma over a time of 10 to 12 years. In any case, in around 10% of patients, sores can advance from in situ to obtrusive in a time of under 1 year. As it becomes intrusive, the growth gets through the cellar film and attacks the cervical stroma. Expansion of the growth in the cervix may at last appear as ulceration, exophytic cancer, or broad penetration of basic tissue, including the bladder or rectum.
Risk Factors;
Expanding age is the main gamble factor for most malignant growths. The essential gamble factor for cervical disease is human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.[3-6]
Other gamble factors for cervical malignant growth incorporate the accompanying:
- High equality and HPV infection.[7]
- Smoking cigarettes and HPV infection.[8]
- Long haul utilization of oral contraceptives and HPV infection.[9,10]
- Immunosuppression.[11,12]
- Having first sexual experience at a youthful age.[13]
- Large number of sexual partners.[13]
- Openness to diethylstilbestrol (DES) in utero.[14].
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection;
HPV contamination is an important stage in the improvement of basically all precancerous and destructive sores. Epidemiological investigations convincingly exhibit that the significant gamble factor for improvement of preinvasive or obtrusive carcinoma of the cervix is HPV disease, far offsetting other realized risk factors.
In excess of 6 million ladies in the US are assessed to be tainted with HPV. Transient HPV disease is normal, especially in youthful women,[15] while cervical malignant growth is uncommon. The tirelessness of a HPV contamination prompts expanded hazard of creating precancerous and dangerous lesions.[16,17]
The kind of HPV contamination is additionally significant in presenting risk. Numerous subtypes of HPV taint people; of these, subtypes 16 and 18 have been generally firmly connected with high-grade dysplasia and disease. Review propose that intense contamination with HPV types 16 and 18 gave a 11-overlap to 16.9-crease hazard of fast improvement of high-grade CIN.[18-20] Further investigations have shown that disease with either HPV 16 or 18 is more prescient than cytological screening of high-grade CIN or more noteworthy sickness, and that the prescient capacity is seen for as long as 18 years after the underlying test.[21-23]
There are two economically accessible immunizations that target anogenital-related types of HPV. The antibodies are coordinated towards HPV-credulous youths and youthful grown-ups. In spite of the fact that entrance of the immunization has been moderate, huge reductions in HPV-related sicknesses have been documented.[24] For more data, see Cervical Cancer Avoidance.
For further details Click Now.
Clinical Features;
Early cervical malignant growth may not cause observable signs or side effects.
Potential signs and side effects of cervical malignant growth incorporate the accompanying:
Vaginal dying.
Surprising vaginal release.
Pelvic torment.
Dyspareunia.
Postcoital dying.
Diagnosis;
The accompanying strategies might be utilized to analyze cervical malignant growth:
History and actual test.
Pelvic test.
Cervical cytology (Pap smear).
HPV test.
Endocervical curettage.
Colposcopy.
Biopsy.








0 Comments